Structure and principle of transformer
Writer: Hengfeng you electric Time:2023-04-20 views:times
The internal structure of the transformer is messy, but in terms of its structural composition, the fundamental structural components of the transformer are iron core and winding. These two primary components constitute the body of the transformer. Different types of transformers will also have insulating bushings, oil conservator, gas relay, safety airway and other accessories.
The fundamental structural components of transformer are iron core and winding, which constitute the body of transformer. In order to improve the heat dissipation conditions, the body of large and medium capacity transformers is immersed in a closed oil tank filled with transformer oil, and the connection between each winding and the external circuit is led out through an insulating sleeve.
In order to make the transformer operate safely and reliably, it is also equipped with accessories such as oil conservator, gas relay and safety airway.
(1)core
The fundamental structural components of transformer are iron core and winding, which constitute the body of transformer. In order to improve the heat dissipation conditions, the body of large and medium capacity transformers is immersed and filled
The iron core is used as the magnetic circuit of the transformer; It also serves as the mechanical framework of the transformer. In order to improve the magnetic conductivity and reduce the loss caused by alternating magnetic flux in the iron core, the iron core of the transformer is made of electrical steel sheets with a thickness of 0.35-0.5mm. Both sides of the electrical steel sheet are coated with insulating layers for insulation. Cold rolled electrical steel sheets with high permeability and low loss are mostly used for large capacity transformers.
The core of power transformer generally adopts core structure, and its core can be divided into core column (part with winding) and iron yoke (part connecting two core columns). The winding is sleeved on the iron core column, and the iron yoke closes the magnetic circuit between the iron core columns. When the iron core column and iron yoke are combined to form the whole iron core, the overlapping assembly is mostly selected, so that the joints of each layer are not at the same address, which can reduce the excitation current, but the disadvantage is that the assembly is messy and time-consuming. In general transformers, the cross-section of core column adopts the stepped shape of circumscribed circle. Only when the transformer capacity is very small, the square is selected.
The communication magnetic flux will cause eddy current loss and hysteresis loss in the iron core, making the iron core hot. In the iron core of large capacity transformer, oil passage is often set. The iron core is immersed in transformer oil. When the oil flows out of the oil passage, the heat in the iron core can be taken away.
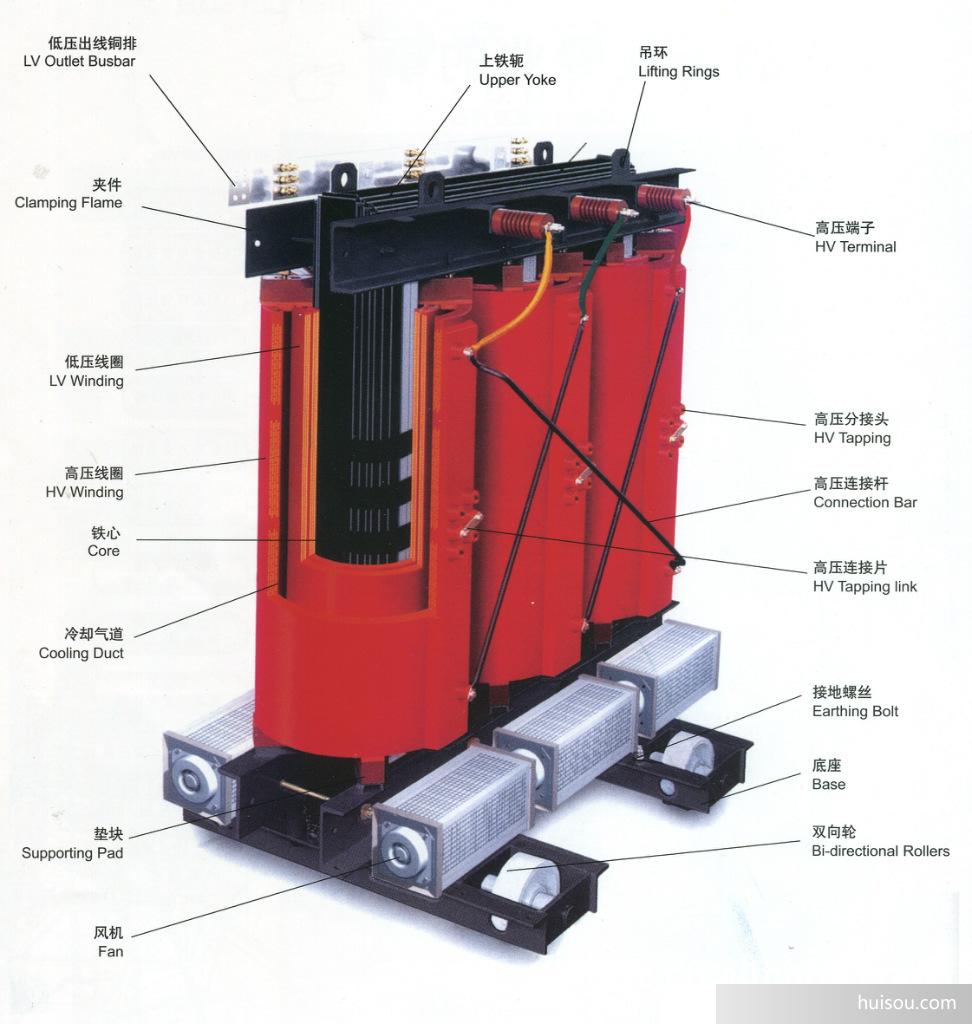
(2) Winding
Winding is the circuit part of transformer, which is used to transmit electric energy. It is generally divided into high-voltage winding and low-voltage winding. The winding connected to higher voltage is called high voltage winding; The winding connected to a lower voltage is called a low voltage winding. In terms of energy conversion and transmission, the winding connected to the power supply and absorbing electric energy from the power supply is called primary winding (also known as primary winding or primary winding); The winding connected with the load and delivering electric energy to the load is called secondary winding (also known as secondary winding or secondary winding). The winding is generally made of insulated copper wire. High voltage winding has many turns and small conductor cross section; Low voltage winding has few turns and large conductor cross section.
In order to ensure the safe and reliable operation and sufficient service life of the transformer, there are certain requirements for the electrical performance, heat resistance and mechanical strength of the winding. The winding is a combination of several coils connected according to a certain law. According to the different positions of high-voltage winding and low-voltage winding, the winding structure can be divided into concentric type and overlapping type. The concentric winding is that the high-voltage winding and low-voltage winding are concentrically sleeved on the iron core column.
For the convenience of insulation, the low-voltage winding is close to the iron core, the high-voltage winding is sleeved outside the low-voltage winding, and an oil passage is reserved between the two windings. The first oil passage is used as the insulation gap between windings; Second, as a heat dissipation channel, the oil flows through the cooling winding from the oil passage. In a single-phase transformer, the high and low voltage windings are divided into two parts, which are respectively sleeved on two core columns, and the two parts can be connected in series or in parallel; In the three-phase transformer, the high and low voltage windings belonging to the same phase are all sleeved on the same core column. The structure of concentric winding is simple and easy to manufacture. This structure is generally used in core transformer.
The overlapping winding is formed by dividing the high-voltage winding and low-voltage winding into several wire cakes and placing them alternately along the iron core column. In order to facilitate insulation and heat dissipation, an oil passage is reserved between the high-voltage winding and the low-voltage winding, and the low-voltage winding is placed at the top and bottom near the iron yoke. Overlapping winding has high mechanical strength and convenient lead. Shell transformer generally adopts this structure.
(3) Oil tank and accessories
1. Oil tank: the oil tank is the shell of the oil immersed transformer. The winding and iron core of the transformer will generate heat during operation. In order to quickly dissipate the heat to the surrounding air, the method of adding heat dissipation area can be adopted. The structural types of transformer oil tank mainly include flat plate type, pipe type, etc.
For transformers with large capacity, a tubular oil tank equipped with a heat dissipation pipe on the outside of the oil tank wall is used to add the heat dissipation area. When the oil is greatly expanded by heat, the hot oil in the tank rises to the upper part of the oil tank, and the oil cooled by the heat dissipation pipe falls to the bottom of the oil tank to form a natural circulation and dissipate the heat into the surrounding air.
For large capacity transformers, forced cooling can also be adopted, such as blowing the transformer with an electric fan to improve the heat dissipation effect. The transformer oil is sheathed on the iron core by high and low voltage windings, which is generally called the body. The body is placed in the oil tank, which is filled with transformer oil.
2. Transformer oil: transformer oil is a kind of mineral oil with good insulation performance. Transformer oil has two effects: ① it has insulation effect between transformer winding and winding, winding and iron core and oil tank to improve the insulation strength of winding. Because oil has better insulation than air. ② The transformer oil generates convection after being heated, which has a heat dissipation effect on the transformer core and winding. Due to the convection effect after being heated by the oil, the heat of the winding and core can be brought to the oil tank wall, and then distributed to the air by the oil tank wall. The requirements for transformer oil are: high dielectric strength; High ignition point; Low viscosity; The content of water and impurities shall be as small as possible.
3. Oil conservator: the transformer oil will swell after heating, so the oil tank cannot be sealed. In order to reduce the contact area between oil and air, the transformer is equipped with an oil conservator. The oil conservator is fixed on the top of the oil tank and directly connected with the oil tank with a pipe. The upper part of the oil conservator is provided with a refueling bolt, which can supplement oil to the transformer, and the lower part of the oil tank is provided with an oil drain valve, which can discharge transformer oil.
The oil conservator isolates the inside of the oil tank from the outside air, reducing the area of oil oxidation and water absorption. The height of the oil level in the oil conservator is controlled within a certain range. When the oil is expanded by heat, part of the oil is squeezed into the oil conservator to raise the oil level. When the oil shrinks when it is cold, this part of the oil flows back to the oil tank to lower the oil level. The size of the oil conservator shall meet the requirements that the oil level of the transformer can always be kept within the range of the oil conservator under various possible operating temperatures. There is an oil level gauge on one side of the oil conservator, which can check the change of oil level height.
In addition, the oil conservator is also equipped with a moisture absorber, which is an air filtering device. The external air can enter the oil conservator only after being dried by the moisture absorber, so that the oil in the oil tank is not easy to deteriorate and damage.
4. Gas relay (gas relay): it is installed in the pipeline between the oil tank and oil conservator of the transformer and is the main protective device. There is a float with a mercury switch and a baffle that can drive the mercury switch. When the transformer breaks down, the gas accumulates in the upper part of the gas relay, the oil level drops, the pontoon sinks, and the mercury switch is turned on to announce the signal; When a serious fault occurs in the transformer, the oil flow breaks through the baffle and the baffle deflects, drive a set of organization to turn on another mercury switch, announce the signal and trip, and cut off the power supply of the transformer.
5. Safety air passage (explosion-proof tube): the oil tank cover of large capacity transformer is also equipped with a safety air passage. It is a long steel cylinder, which is connected with the oil tank below and equipped with an explosion-proof membrane at the upper end. When serious problems occur inside the transformer and a lot of gas occurs, the pressure inside the oil tank rises rapidly and breaks through the explosion-proof membrane on the safety airway to eject gas and eliminate the pressure, so as to avoid major accidents.
6. Tap changer: in the power system, in order to control the output voltage of the transformer within the allowable variation range, the turns of the primary winding of the transformer shall be adjusted within a certain range. Therefore, the primary winding is generally equipped with taps, which are called taps. The number of turns of the original winding can be changed by connecting the switch with different joints to achieve the purpose of voltage regulation. Tap changer is divided into on load tap changer and off load tap changer.
7. Insulating sleeve: it is installed on the oil tank cover of the transformer to lead out the coil lead end from the oil tank and insulate the lead from the oil tank. Porcelain insulating bushing is used for voltage lower than 1kV, inflatable or oil filled bushing is used for voltage between 10-35kV, and capacitive bushing is used for voltage higher than 110kV.
8. Temperature measuring device: monitor the oil level temperature of transformer. Mercury thermometers are used for small oil immersed transformers and pressure thermometers are used for larger transformers.


